Mycoplasma Detection, Removal and Prevention
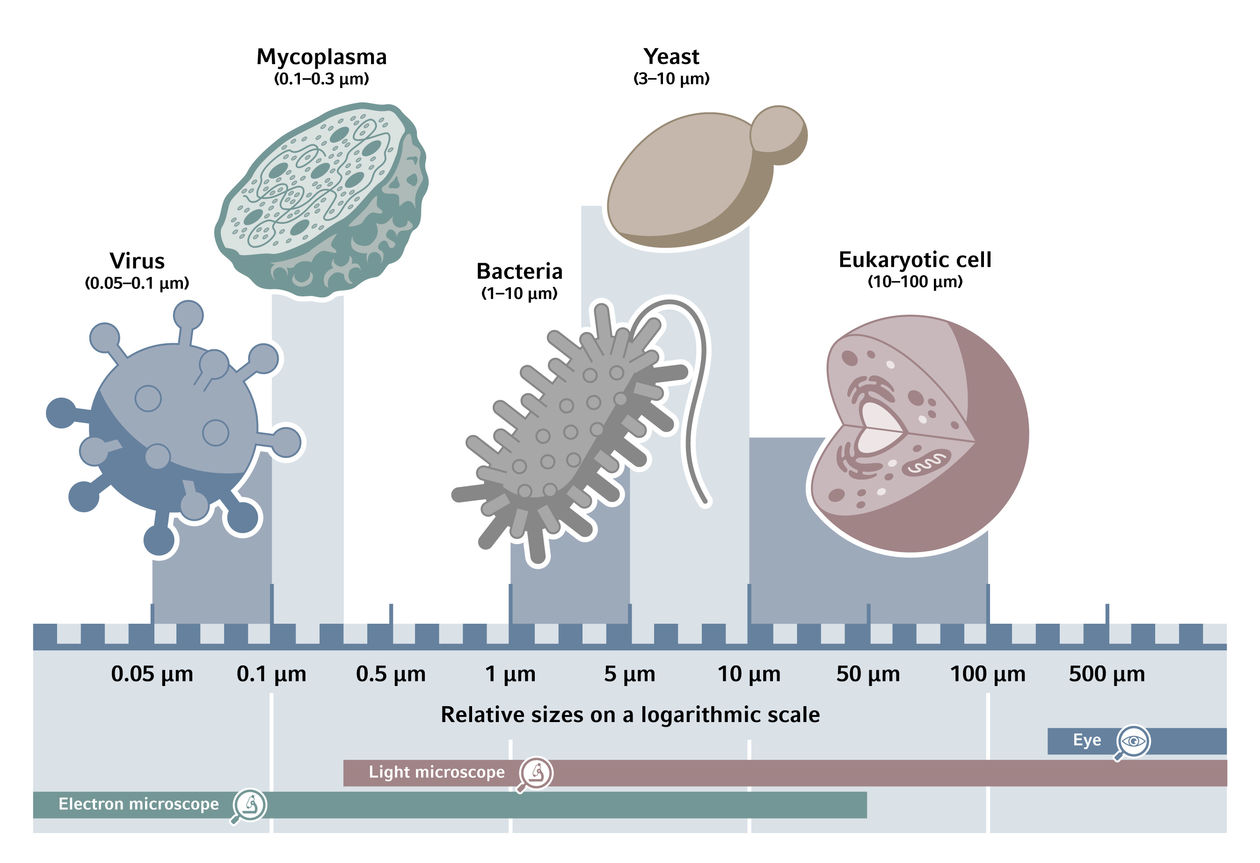
Cell biology is a scientific discipline that focuses on the study of cells, their physiological properties, structure, and functions. It encompasses a wide range of topics, including cell structure, organelles, cell metabolism, cell cycle, cell signaling, and cell communication. Cell biologists utilize various techniques such as microscopy, cell culture, molecular biology, and biochemistry to investigate cellular processes and understand how cells function, interact, and contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms. The field of cell biology plays a critical role in advancing our understanding of various biological phenomena, including development, disease mechanisms, and the functioning of tissues and organs.
Detection-PCR
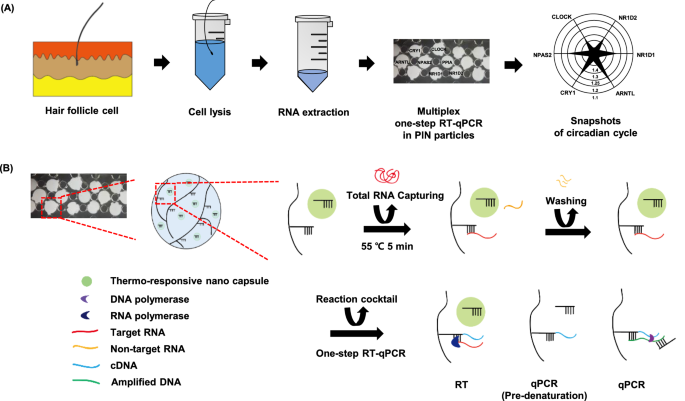
PCR detection involves the use of the polymerase chain reaction technique to amplify specific DNA sequences for analysis, providing a sensitive method for detecting and quantifying DNA samples.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences. The PCR reaction uses a DNA polymerase enzyme to create copies of a DNA target sequence. The PCR reaction is repeated many times, resulting in the exponential amplification of the target sequence. This makes it possible to detect very small amounts of DNA.
Basement Membrane Matrix
Conventional Type
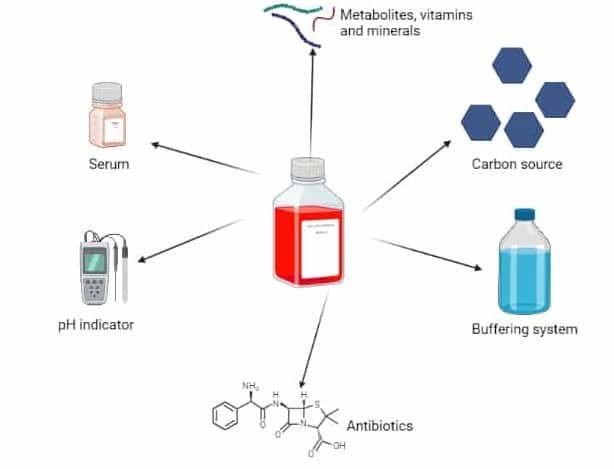
The conventional type refers to standard cell culture media that support the growth and maintenance of various cell types under typical laboratory conditions, providing essential nutrients and factors for cellular proliferation and viability.
Conventional Phenol Red-Free:
Conventional phenol red-free media offer a standard cell culture environment without phenol red, allowing for the cultivation of cells without the interference of this pH indicator, suitable for sensitive applications and specialized experimental requirements.
Biological Drug Quality Control
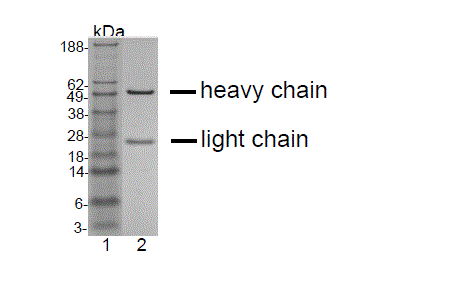
HCD Detection
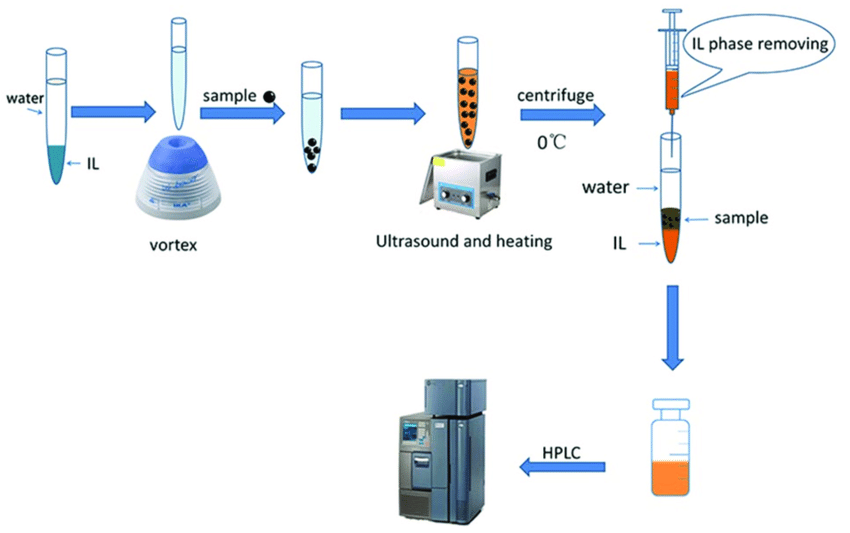
HCD Detection Heavy-chain detection (HCD) is a method for detecting nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA, in a sample. It is based on the use of antibodies that specifically bind to the heavy chains of immunoglobulins (IgGs). When HCD is used in conjunction with a polymerase chain reaction (PCR), it can be used to detect very small amounts of DNA or RNA.
HCD is a powerful tool that can be used for a variety of applications, including:
- Detecting pathogens: HCD can be used to detect the presence of pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria, in a sample.
- Detecting cancer cells: HCD can be used to detect the presence of cancer cells in a sample.
- Monitoring gene expression: HCD can be used to monitor the expression of specific genes in a sample.
HCD is a relatively new technology, but it has already shown great promise for a variety of applications. It is likely to become an increasingly important tool for researchers and clinicians in the years to come.