mRNA-Based Therapy: A Revolutionary Approach to Treating Disease
Discover the groundbreaking world of mRNA-based therapy, a revolutionary approach to treating diseases. Explore its advantages, applications, and potential to transform medicine.
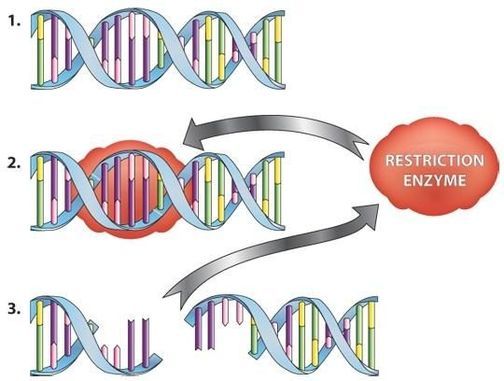
Restriction Enzyme Digestion
Restriction enzyme digestion is a molecular biology technique used to cleave DNA at specific recognition sequences, facilitating various downstream applications such as cloning, DNA mapping, and genetic analysis. Here are some essential details about restriction enzyme digestion:
- Workflow Overview: The technique involves incubating DNA with specific restriction enzymes that recognize and cut DNA at particular nucleotide sequences, generating fragments of various sizes based on the location of the recognition sites.
- Enzyme Selection and Incubation: Choose the appropriate restriction enzymes based on the target DNA sequence and experimental requirements. Incubate the DNA with the selected enzymes under controlled conditions to ensure optimal cleavage efficiency and specificity.
- Reaction Conditions: Maintain suitable reaction conditions, including buffer composition, pH, temperature, and duration of incubation, as recommended by the enzyme supplier or established protocols, to achieve precise and consistent DNA cleavage.
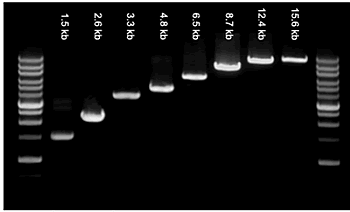
- Gel Electrophoresis: Analyze the digested DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis to separate the fragments based on their size, allowing for the visualization and verification of the digestion pattern and the identification of specific DNA fragments.
- Purification and Extraction: Purify the digested DNA fragments using suitable purification methods, such as gel extraction or column-based techniques, to isolate and recover the desired DNA fragments for subsequent applications.
- Data Interpretation and Analysis: Analyze the digested DNA fragments to decipher the genetic information encoded within the sequence, providing valuable insights into the structural and functional aspects of the DNA molecule under investigation.
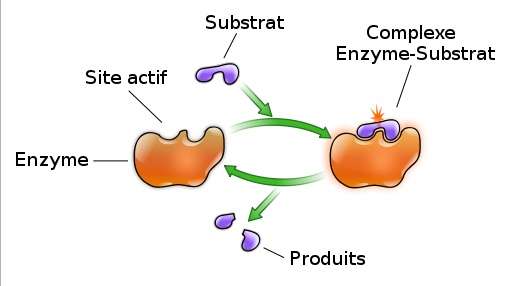
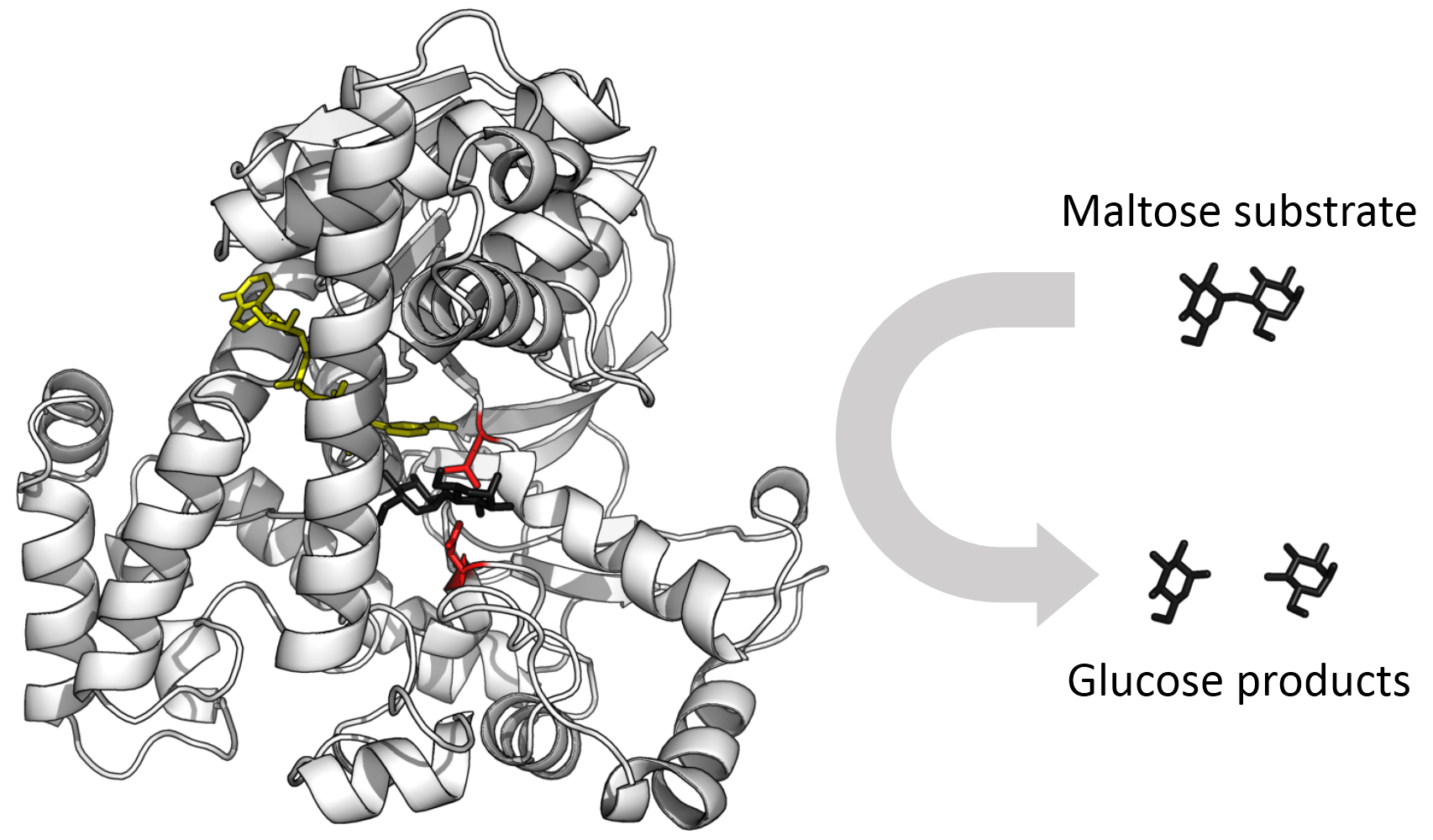
Enzyme
Gentaur offers a wide range of enzymes for various applications in life science research and diagnostics. Their enzymes are known for their high purity, activity, and stability.
Key Features:
- High Purity: Gentaur enzymes undergo rigorous purification processes to ensure their purity and minimal contamination.
- High Activity: Gentaur enzymes exhibit high catalytic activity, ensuring efficient and effective enzymatic reactions.
- Stability: Gentaur enzymes are designed to maintain their activity and stability under various experimental conditions.
Applications:
- Molecular Biology: Gentaur enzymes are widely used in molecular biology techniques, such as PCR, RT-PCR, and DNA sequencing.
- Protein Research: Gentaur enzymes are essential tools for protein purification, characterization, and modification studies.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): Gentaur enzymes are crucial components in ELISA kits for detecting and quantifying various analytes.
- Diagnostics: Gentaur enzymes are employed in diagnostic tests for detecting diseases, genetic disorders, and infections.
Examples of Gentaur Enzymes:
- DNA Polymerases: Enzymes for DNA amplification and synthesis.
- Restriction Enzymes: Enzymes for cutting DNA at specific recognition sites.
- Reverse Transcriptases: Enzymes for converting RNA to DNA.
- Ligases: Enzymes for joining DNA fragments together.
- Proteases: Enzymes for breaking down proteins.
- Phosphatases: Enzymes for removing phosphate groups from proteins.
Advantages of Gentaur Enzymes:
- High quality and reliability for consistent results.
- Broad range of enzymes for diverse applications.
- Competitive pricing and bulk discounts available.
Overall, Gentaur enzymes are valuable tools for researchers and scientists working in various fields of life science research and diagnostics.
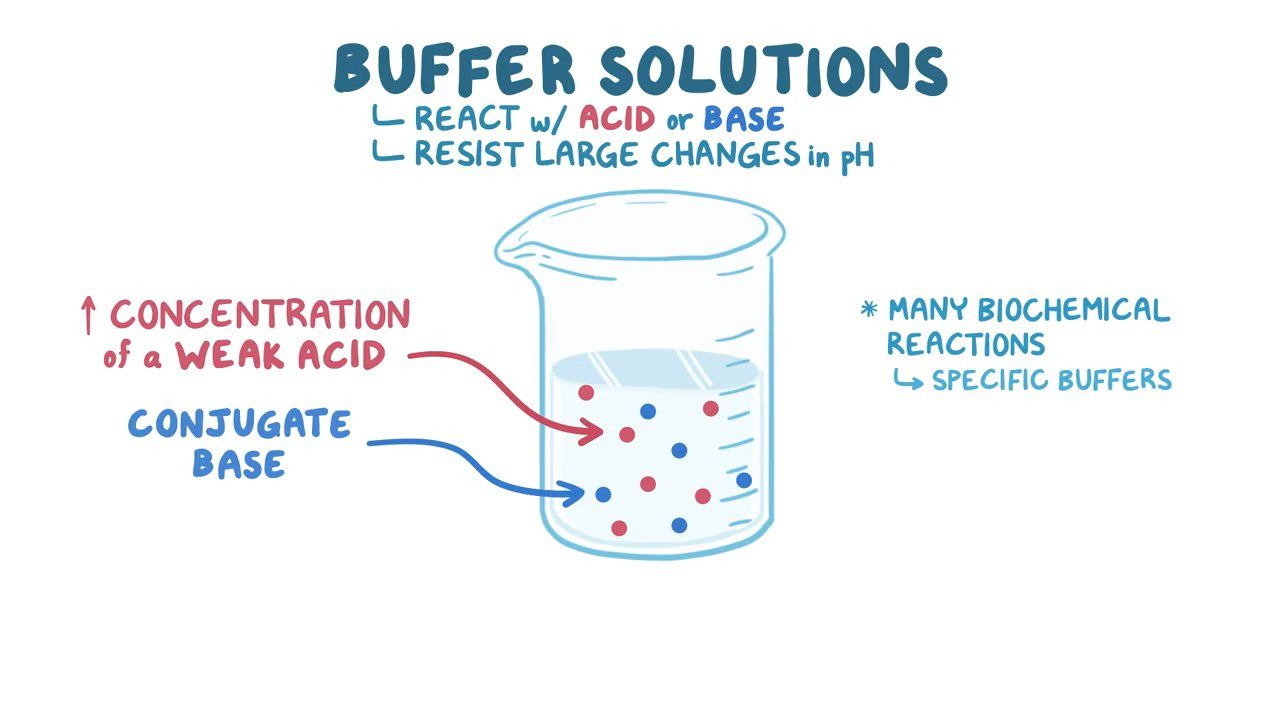
Buffer
Gentaur manufactures a wide range of buffers for various applications in biology and molecular biology. Their buffers are formulated with high-quality components and undergo rigorous testing to ensure consistent performance.
Key Features:
- Precise pH Control: Gentaur buffers are precisely adjusted to maintain the desired pH, crucial for enzymatic reactions and maintaining protein stability.
- High Solubility: Gentaur buffers are designed to efficiently dissolve various biomolecules and reagents, ensuring their proper functioning in experiments.
- Stability: Gentaur buffers are formulated to maintain their composition and pH stability over time, ensuring consistent results.
Applications:
- Enzyme Reactions: Gentaur buffers provide the optimal pH and ionic environment for enzymatic reactions, ensuring their efficiency and accuracy.
- Protein Purification: Gentaur buffers are essential for protein purification and isolation, maintaining protein stability and preventing degradation.
- Electrophoresis: Gentaur buffers are used in electrophoresis techniques, such as SDS-PAGE and DNA agarose gel electrophoresis, to separate and analyze biomolecules.
- Nucleic Acid Manipulation: Gentaur buffers are employed in various nucleic acid manipulation techniques, such as PCR, restriction digestion, and ligation, ensuring optimal conditions for these processes.
Examples of Gentaur Buffers:
- Tris-HCl Buffers: Versatile buffers used for a wide range of applications, including enzyme reactions, protein purification, and electrophoresis.
- PBS (Phosphate-Buffered Saline): A commonly used physiological buffer for maintaining cell viability and function in experiments.
- Stop Buffers: Buffers used to inactivate enzymes and stabilize proteins or nucleic acids after specific reactions.
- Binding Buffers: Buffers optimized for binding interactions, such as antibody-antigen binding in ELISA or immunoprecipitation assays.
- Elution Buffers: Buffers designed to elute bound molecules from resins or matrices, such as proteins from affinity chromatography columns.
Advantages of Gentaur Buffers:
- High quality and consistency for reliable results.
- Wide range of buffers for diverse applications.
- Convenient packaging options and bulk discounts available.
Overall, Gentaur buffers are essential reagents for researchers and scientists working in various fields of biology and molecular biology.
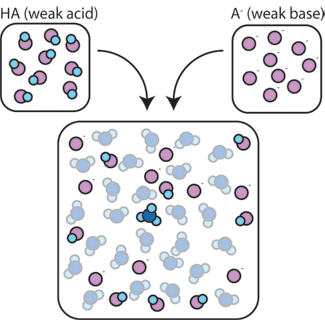
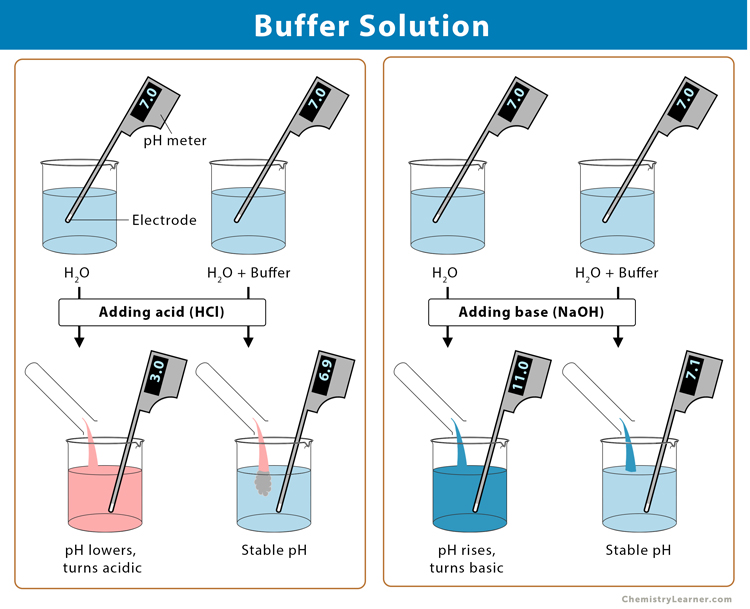
A buffer is a solution that helps stabilize the pH level, maintaining it within a specific range despite the addition of acids or bases. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid, ensuring that the pH remains relatively constant even when exposed to external factors. Buffers play a crucial role in various biochemical and chemical processes, including enzymatic reactions, cell culture, and molecular biology experiments, where maintaining a stable pH is essential for optimal performance and reproducibility.
In Vitro Transcription
A synthesis kit refers to a collection of tools and reagents used to construct various molecules, such as DNA, RNA, or proteins, through a controlled chemical or enzymatic process. These kits typically include necessary components like primers, enzymes, nucleotides, and buffers, allowing researchers to synthesize specific molecules for diverse applications, including cloning, PCR, transcription, and translation. They are designed to streamline the synthesis process, ensuring efficiency and reproducibility in various molecular biology experiments and enabling researchers to generate custom molecules tailored to their specific research needs.
NTP
Sodium Solution
Sodium solution is a common laboratory reagent used in various biological and chemical applications. Gentaur offers high-purity sodium solutions in various concentrations and formats.
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Solution: This commonly used salt solution is available in various concentrations, such as 0.9% (physiological saline) and 5M.
- Sodium Acetate (NaAc) Solution: This solution is used as a buffer and precipitating agent in various biochemical and analytical techniques.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) Solution: This strong alkaline solution is used for various applications, including pH adjustment, hydrolysis reactions, and metal cleaning.
- Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) Solution: This anionic detergent is widely used in protein denaturation and electrophoresis techniques.
Tris Solution
Tris solution is a versatile buffer commonly used in molecular biology and biochemistry. Gentaur offers high-quality Tris solutions in various concentrations and pH ranges.
- Tris-HCl Buffer: This is the most common Tris buffer, available in various concentrations (e.g., 10 mM, 50 mM, 1 M) and pH ranges (e.g., pH 7.5, pH 8.0).
- Tris-Base Solution: This concentrated Tris solution is used to prepare Tris-HCl buffers at specific pH values.
- Tris-EDTA Buffer (TE Buffer): This buffer is commonly used for storing and manipulating DNA and RNA samples.
- Tris-Glycine Buffer (TBE Buffer): This buffer is widely used for DNA electrophoresis and Southern blots.

Sodium Solution
Sodium solutions are commonly used as reagents in biological and chemical applications, with various concentrations available to facilitate specific experimental requirements. They are utilized in buffer preparations, protein purification, and cell culture techniques, among other applications.

Tris Solution
Tris (tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane) solutions are buffer solutions commonly employed in biological and biochemical experiments. Tris solutions are formulated to maintain a stable pH environment for enzymatic reactions, electrophoresis, and nucleic acid and protein isolation and analysis. They are available in different concentrations and pH levels to suit diverse experimental needs.
Capping Reaction
In molecular biology, capping reaction refers to the process of adding a 7-methylguanosine "cap" to the 5' end of an RNA molecule, aiding in its stability and efficient translation. This modification is crucial for mRNA maturation and protects the RNA from degradation.

Methyl Donor
Methyl donors are compounds that contribute methyl groups (CH3) to various substrates, facilitating methylation reactions. They are essential for DNA and histone methylation, regulating gene expression and chromatin structure. Common methyl donors include S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and folate, playing critical roles in various cellular processes.

Buffer
Buffers are solutions that help maintain the pH of a system, stabilizing it against changes in acidity or alkalinity. In the context of capping reactions, buffers ensure optimal enzymatic activity and stability, promoting efficient RNA capping processes by maintaining a favorable pH environment.

Enzyme
Enzymes involved in capping reactions are primarily RNA capping enzymes, responsible for catalyzing the addition of the 7-methylguanosine cap to the 5' end of mRNA. These enzymes exhibit specific triphosphatase, guanylyl transferase, and guanine methyltransferase activities, collectively contributing to the capping process essential for mRNA maturation and function.