RNase inhibitor
Inhibits various RNases
Free of nuclease contamination and residual bacterial DNA
RNase inhibitor
Murine RNase inhibitor is a recombinant protein that protects RNA from degradation by binding to RNase A, B, or C. It is more stable than human RNase inhibitors at low DTT concentrations, making it suitable for use in reactions where high DTT concentrations interfere with the reaction, such as real-time RT-PCR.
And protects RNA from degradation and is more stable than human RNase inhibitors at low DTT concentrations, making it suitable for use in real-time RT-PCR and other reactions where high DTT concentrations interfere.
Safeguarding RNA Integrity: Unveiling the Significance of RNase Inhibitor
Introduction:
In the delicate realm of RNA research, where precision and integrity are paramount, the role of RNase inhibitor stands as a guardian against the threat of RNA degradation. This essential enzyme inhibitor is a linchpin in preserving the quality of RNA samples, ensuring that researchers can extract reliable and undamaged genetic information.
Key Functions:
**1. RNase Protection: RNase inhibitor serves as a sentinel, shielding RNA molecules from the enzymatic activity of ribonucleases (RNases). Its primary function lies in preventing the degradation of RNA, allowing researchers to obtain accurate and unaltered genetic information.
**2. Versatility in Applications: From basic molecular biology experiments to complex RNA-based assays, the versatility of RNase inhibitor makes it a cornerstone in diverse applications. It finds utility in cDNA synthesis, in vitro transcription, and RNA purification protocols, ensuring the fidelity of RNA-based analyses.
**3. Stability Across Conditions: RNase inhibitor demonstrates remarkable stability across a spectrum of experimental conditions. Its resilience in the face of varying temperatures and reaction environments makes it a dependable ally for researchers working on a broad range of RNA-related studies.
Advantages:
**1. Preservation of RNA Quality: The primary advantage of employing RNase inhibitor lies in its ability to preserve the quality of RNA samples. By neutralizing the activity of RNases, it safeguards RNA integrity, providing researchers with reliable templates for downstream applications such as RT-qPCR, RNA sequencing, and gene expression studies.
**2. Enhanced Sensitivity: RNase inhibitor enhances the sensitivity of RNA-based assays by preventing unwanted RNA degradation. This is particularly crucial in experiments where the starting material is limited, ensuring that researchers can extract maximum information from precious samples.
**3. Consistency Across Experiments: Researchers can rely on the consistency offered by RNase inhibitor, ensuring reproducibility across experiments. This is vital for longitudinal studies, large-scale analyses, and any research endeavor where data consistency is paramount.
Applications:
**1. Molecular Biology Techniques: In standard molecular biology techniques like reverse transcription and PCR, RNase inhibitor plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of RNA templates. Its inclusion in reaction mixtures ensures the accuracy of results, even in the presence of trace contaminants.
**2. Cell Culture Work: In cell culture studies where RNA is extracted from cultured cells, the addition of RNase inhibitor becomes indispensable. It prevents the degradation of RNA during the isolation process, enabling researchers to obtain high-quality RNA for subsequent analyses.
**3. In Vitro Transcription: For researchers involved in in vitro transcription experiments, RNase inhibitor is a crucial component. It ensures the stability of RNA transcripts, allowing for reliable and consistent results in studies involving RNA synthesis.
Conclusion:
RNase inhibitor stands as a silent yet indispensable guardian, fortifying the foundations of RNA research. Its role in preserving RNA integrity, enhancing sensitivity, and ensuring consistency across experiments elevates it to a critical position in the toolkit of molecular biologists. As researchers delve into the intricacies of RNA-based investigations, the significance of RNase inhibitor becomes clear—a defender of genetic information, allowing the symphony of RNA research to unfold with accuracy and reliability.
Product Information
| Catalog | Name | Size | RNase Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBP000401 | RNase Inhibitor | 2.5KU/0.0625mL | Yes |
| HBP000402 | RNase Inhibitor | 10KU/0.25mL | Yes |
| HBP000403 | RNase Inhibitor | 400KU/10mL | Yes |
| HBP000404 | RNase Inhibitor | 4000KU/100mL | Yes |
| HBP000405 | RNase Inhibitor | 40000KU/1000mL | Yes |
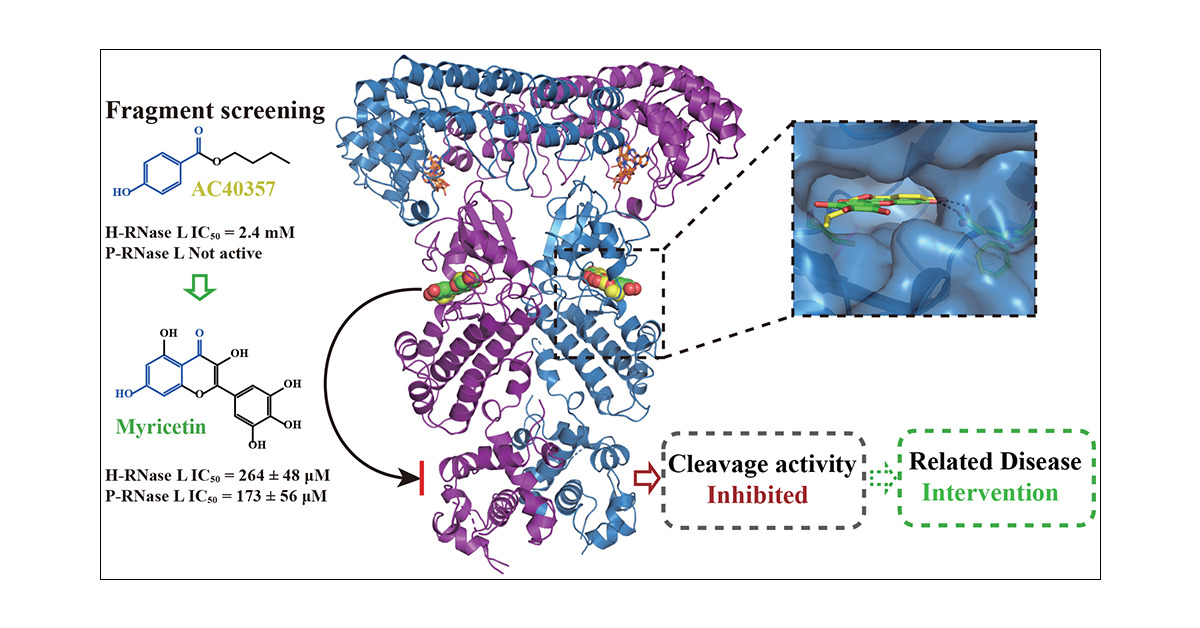
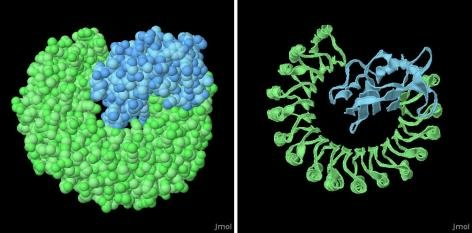
The composite architecture of RNase A in conjunction with Ribonuclease inhibitor is visually depicted in this illustration, sourced from the Protein Data Bank (PDB-101). The figure captures the intricate interplay between RNase A, an enzyme central to RNA degradation, and Ribonuclease inhibitor, a molecular bodyguard against its catalytic activity. This structural amalgamation offers a nuanced glimpse into the dynamic molecular dance where the inhibitor aptly shields RNA from the cleaving prowess of RNase A. As a snapshot of their complex interaction, this figure provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms that underpin RNA integrity preservation, adding to the wealth of knowledge in the field of structural biology.
Features
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Storage | -20°C for up to 2 years |
| Buffer | 50 mM KCl, 20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.6, 25°C), 8 mM DTT, and 50% glycerol |
| Unit definition | One unit (U) is defined as the amount of murine RNase inhibitor required to inhibit the activity of 5 ng of ribonuclease A by 50%. |
| Molecular weight | 50 kDa |
| Quality control | Exonuclease, endonuclease, nicking, and RNase activities are all absent. E. coli genomic DNA contamination is ≤ 1 E. coli genome. |
| Applications | Protecting RNA from degradation during cDNA synthesis, RT-PCR, RT-qPCR, in vitro transcription/translation, and RNA separation and purification. |
| Usage notes | Avoid violent oscillation or stirring, as this can inactivate the enzyme. The optimal temperature range for the inhibitor is 25-55°C. It is inactivated at 65°C and above. Murine RNase inhibitor does not inhibit RNase H, RNase 1, or RNase T1. The inhibitor is active over a wide pH range (pH 5-9), with highest activity at pH 7-8. Avoid denaturing temperatures and high concentrations of urea or other denaturing agents, as these can release active ribonuclease. |
| Additional notes | Murine RNase inhibitor is a versatile and useful tool for protecting RNA from degradation. It is especially useful for applications where high DTT concentrations are not compatible. When using murine RNase inhibitor, it is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. |
Applications
Murine RNase inhibitor can be used in a wide range of experiments to protect RNA from degradation, including:
- Synthesis of cDNA, RT-PCR, and RT-qPCR
- In vitro transcription/translation (e.g., in vitro viral replication system)
- RNA separation and purification
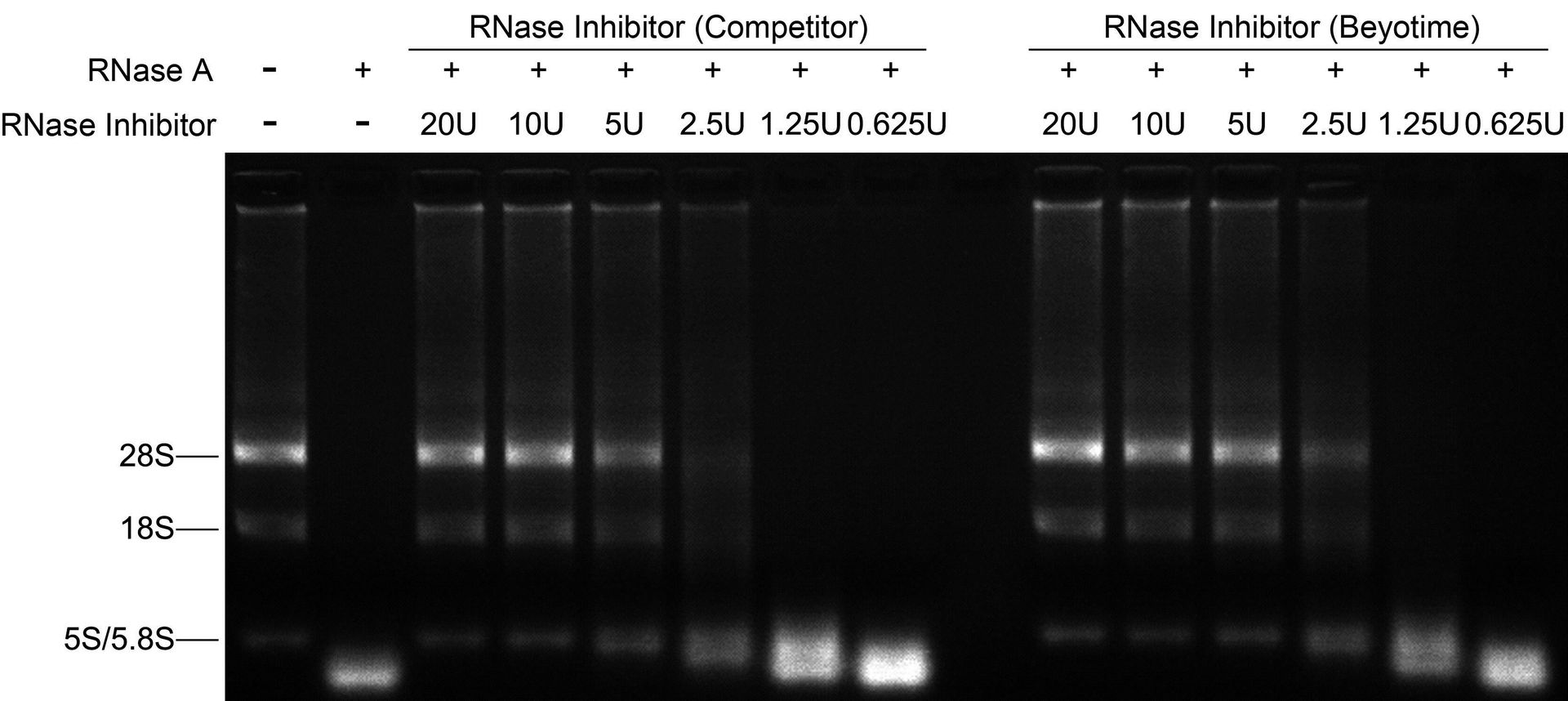
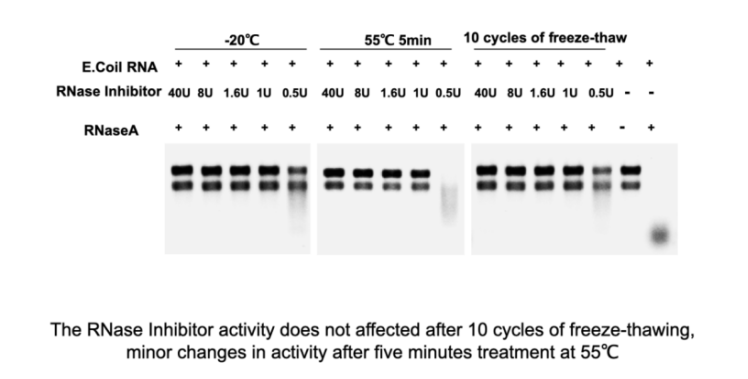
Summary of the test results for murine RNase inhibitor:
- Exonuclease activity: None detected
- Endonuclease activity: None detected
- Nicking activity: None detected
- RNase activity: None detected
- E. coli genomic DNA contamination: ≤ 1 E. coli genome
These results indicate that murine RNase inhibitor is a highly pure and active enzyme that is effective in inhibiting a wide range of RNases.
In addition to the above tests, murine RNase inhibitor has also been tested in a variety of downstream applications, such as RT-PCR, RT-qPCR, and in vitro transcription. These tests have shown that murine RNase inhibitor is compatible with a variety of commercial reagents and produces high-quality results.
Overall, the test results for murine RNase inhibitor are very positive. This enzyme is a valuable tool for protecting RNA from degradation in a variety of molecular biology applications.