Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5%: Unveiling the Power of Exceptional Buffering
Delve into the realm of Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5%, a highly purified and versatile buffering agent that has revolutionized biological research. Discover its exceptional pH control capabilities, extensive applications, and ease of use, making it an indispensable tool for scientists and researchers alike.
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5%: A Versatile Buffer for Biological Applications
Imidazole, a heterocyclic organic compound, has gained prominence in molecular biology due to its exceptional buffering capabilities and diverse applications in biological research. Imidazole for molecular biology, specifically the 99.5% pure form, is a highly sought-after reagent for various biochemical and analytical techniques.
Buffering Capacity and Applications
Imidazole's buffering capacity stems from its ability to accept and donate protons, effectively regulating the pH of solutions. This buffering property makes it an invaluable tool in maintaining stable pH conditions for biological reactions and processes. In molecular biology, imidazole is commonly used as a buffer for:
- Enzyme Assays: Imidazole maintains the optimal pH for enzyme activity, ensuring accurate enzyme kinetics studies and protein characterization.
- Nucleic Acid Purification: Imidazole buffers are used in nucleic acid purification protocols, preventing nucleic acid degradation and ensuring their integrity during extraction and isolation procedures.
- Protein Solubilization: Imidazole can promote protein solubilization, helping to keep proteins in solution for further analysis and manipulation.
- Cell Culture: Imidazole can be used as a buffer component in cell culture media, maintaining the pH balance and supporting cellular growth and viability.
Advantages of Imidazole for Molecular Biology
The 99.5% pure form of imidazole for molecular biology offers several advantages over other buffering agents:
- Wide pH Range: Imidazole effectively buffers solutions over a wide pH range, making it versatile for various applications.
- Low Volatility: Imidazole's low volatility ensures minimal evaporation and pH fluctuations during experiments.
- Compatibility with Biological Molecules: Imidazole is generally compatible with a wide range of biological molecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and enzymes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Imidazole is relatively inexpensive compared to other buffering agents, making it a cost-effective choice for routine laboratory procedures.
Safety Considerations
While imidazole is generally considered safe, it is important to handle it with care as it is a mild irritant to skin and eyes. Appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat, should be worn when working with imidazole.
Table: Storage and Packaging Details
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Storage | Room Temperature |
| Shelf Life | 60 Months |
| IMDG Identification | UN No.: 2923, IMCO Class No.: 8(6.1), Packing Group: III |
| HSN Code | |
| 100 Gms | 29332990 (GST 18%) |
| 25 Gms | 29332990 (GST 18%) |
| 500 Gms | 29332990 (GST 18%) |
| Type of Packing | |
| 100 Gms | Glass Bottle |
| 25 Gms | Glass Bottle |
| 5 Gms | Glass Bottle |
| 500 Gms | Glass Bottle |
Storage and Handling
Proper storage and handling are crucial to maintain the quality of imidazole for molecular biology. It should be stored at room temperature in a tightly sealed container away from direct sunlight and moisture. Under proper storage conditions, imidazole remains stable for several years.
Conclusion
Imidazole for molecular biology, particularly the 99.5% pure form, has established itself as an essential reagent in biological research. Its exceptional buffering capacity, wide pH range, and compatibility with biological molecules make it an invaluable tool for various biochemical and analytical techniques. With its ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and overall versatility, imidazole continues to empower researchers and scientists in their pursuit of biological insights.
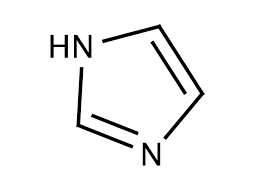
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, with a purity level of 99.5%, stands as a paramount reagent in the realm of molecular biology and biochemistry. Characterized by its distinct five-membered aromatic ring structure, featuring nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3, this compound exhibits versatility and utility across various laboratory applications. The designation "99.5%" underscores the exceptionally high purity of the imidazole, ensuring a premium quality that is well-suited for precise and reliable results in molecular biology experiments.
One of the primary applications of Imidazole in molecular biology is its role as a buffering agent. In this capacity, it contributes to maintaining a stable pH environment, proving invaluable in techniques such as electrophoresis and chromatography. Furthermore, Imidazole's significance extends to protein purification methodologies, particularly in the purification of polyhistidine-tagged proteins. Its ability to coordinate with metal ions, notably nickel, makes it a key component in the elution step during protein purification processes.
Imidazole's prowess in solubilizing proteins further enhances its utility in molecular biology laboratories. Leveraging its unique properties, researchers and scientists rely on this compound to facilitate biochemical reactions and ensure the solubility of proteins critical to their experimental protocols. When working with Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5%, researchers must adhere to stringent safety protocols, employing appropriate protective measures and conducting experiments in well-ventilated laboratory settings. As a cornerstone reagent in molecular biology, Imidazole at this high purity level exemplifies its indispensable role in advancing scientific exploration and discovery.

| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance (Colour) | White |
| Appearance (Form) | Crystalline Powder |
| Solubility (Turbidity) 10% aq. solution | Clear |
| Solubility (Colour) 10% aq. solution | Colourless |
| Assay | min. 99.5% |
| pH (5% aq. solution) | 9.5 - 11.0 |
| Melting Point | 89 - 90°C |
| Sulphated Ash | max. 0.1% |
| Chloride (Cl) | max. 0.005% |
| Sulphate (SO4) | max. 0.005% |
| Iron (Fe) | max. 0.0005% |
| Heavy Metals (Pb) | max. 0.0005% |
| Absorbance (A) of 5% aq. solution in a 1cm cell v/s H2O | |
| @260nm | max. 0.1 |
| @280nm | max. 0.1 |
| @324nm | max. 0.05 |
| Water (KF) | max. 0.5% |
| DNase, RNase, Protease | Not Detected |
Imidazole for Molecular Biology: A Versatile Reagent for Molecular Biology Research
Imidazole, a heterocyclic compound with the molecular formula C3H4N2, is a ubiquitous molecule with a diverse range of applications in the realm of molecular biology. Its unique properties, including its amphoteric nature, high solubility, and ability to chelate metal ions, make it an indispensable tool for researchers working in various fields of biochemistry, enzymology, and biotechnology.
Chemical Properties and Structure
Imidazole is a five-membered aromatic heterocycle with two nitrogen atoms positioned in a 1,3-diazoline configuration. This arrangement endows imidazole with remarkable stability and reactivity. Its pKa value of 6.85 classifies it as a weak base, enabling it to act as both a proton acceptor and a proton donor in various chemical reactions.
Buffering Capacity
Imidazole serves as an excellent buffer due to its ability to maintain a stable pH within a physiological range. Its pKa value falls within the physiological pH range of 6.0 to 8.0, making it ideal for preparing buffers for various molecular biology experiments, such as enzyme assays, protein purification, and DNA manipulation.
Elution Agent in Histidine-Tagged Protein Purification
Imidazole plays a crucial role in purifying histidine-tagged proteins using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC). Histidine-tagged proteins are engineered to possess a sequence of histidine residues at their N-terminus or C-terminus. These histidine residues bind to nickel or cobalt ions immobilized on a chromatography resin. By introducing imidazole into the eluent, the histidine residues are preferentially released from the metal ions, allowing for the elution of the histidine-tagged protein.
Protein Stabilizer
Imidazole's ability to interact with proteins and its amphoteric nature make it an effective protein stabilizer. It prevents proteins from unfolding and aggregating, thereby preserving their structure and function. Imidazole is particularly effective at stabilizing proteins rich in histidine residues due to its specific affinity for these amino acids.
Additional Applications
In addition to its primary roles as a buffer, elution agent, and protein stabilizer, imidazole finds applications in various other areas of molecular biology:
- Enzyme Inhibitor: Imidazole can inhibit the activity of certain enzymes, such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP), by interfering with their active sites.
- Reverse Staining of SDS-PAGE Gels: Imidazole can be used to reverse stain SDS-PAGE gels for protein detection. It enhances the visibility of proteins by reacting with their constituent amino acids, producing a visible signal.
Purity and Quality Assurance
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5% is a highly purified form of imidazole, ensuring minimal contamination with other compounds that could interfere with molecular biology experiments. Stringent quality control measures are implemented during the manufacturing process to guarantee consistent purity and performance.
Conclusion
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5% stands as a versatile and essential reagent for researchers in various fields of molecular biology. Its high purity, unique properties, and wide range of applications make it a staple in many molecular biology laboratories. Whether preparing buffers, purifying proteins, or stabilizing enzymes, imidazole continues to play a critical role in advancing molecular biology research.
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5%: A Versatile Reagent for Molecular Biology
Imidazole is a heterocyclic compound with the molecular formula C3H4N2. It is a white, crystalline solid with a melting point of 91°C and a boiling point of 256°C. Imidazole is soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol.
Imidazole is a versatile reagent with a wide range of applications in molecular biology. It is commonly used as a buffer, an elution agent, and a stabilizer for proteins.
Buffering Agent
Imidazole is an excellent buffer because it has a pKa of 6.85, which is within the physiological pH range of 6.0 to 8.0. This makes imidazole ideal for preparing buffers for various molecular biology experiments, such as enzyme assays, protein purification, and DNA manipulation.
Elution Agent
Imidazole is commonly used as an elution agent for purifying histidine-tagged proteins using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC). Histidine-tagged proteins are proteins that have been engineered to have a sequence of histidine residues at their N-terminus or C-terminus. These histidine residues bind to nickel or cobalt ions that are immobilized on a chromatography resin. Imidazole then competes with the histidine residues for the nickel or cobalt ions, causing the elution of the histidine-tagged protein.
Protein Stabilizer
Imidazole is also used as a stabilizer for proteins. It can prevent proteins from unfolding and aggregating, which can lead to loss of activity. Imidazole is particularly effective at stabilizing proteins that are rich in histidine residues.
Other Applications
In addition to its use as a buffer, elution agent, and protein stabilizer, imidazole has a number of other applications in molecular biology, including:
- Inhibition of enzymes: Imidazole can inhibit some enzymes, such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP).
- Reverse staining of SDS-PAGE gels: Imidazole can be used to reverse stain SDS-PAGE gels for protein detection.
Purity
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5% is a highly purified form of imidazole. This high purity ensures that the imidazole will not introduce any impurities that could interfere with molecular biology experiments.
Conclusion
Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5% is a valuable reagent for researchers working in various fields of molecular biology. Its high purity, versatility, and consistent performance make it a staple in many molecular biology laboratories.
Imidazole is a versatile chemical compound often used in molecular biology and biochemistry. It is a five-membered aromatic ring with two nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3, which contribute to its unique properties. Imidazole is commonly employed for various purposes in molecular biology, and when specified as "for Molecular Biology, 99.5%," it indicates a high purity level suitable for laboratory and research applications.
Here are some key points about Imidazole for Molecular Biology, 99.5%:
- Purity:
- The "99.5%" specification denotes the purity of the imidazole, indicating that 99.5% of the substance in the sample is imidazole. High purity is crucial for molecular biology applications to ensure accurate and reliable results.
- Application:
- Imidazole is often used in molecular biology for its ability to act as a buffer and to facilitate various biochemical reactions.
- It is commonly used in protein purification techniques, including polyhistidine-tagged protein purification, as it can bind to metal ions such as nickel.
- Buffering Agent:
- Imidazole is frequently employed as a buffer component in electrophoresis and chromatography techniques, helping to maintain a stable pH environment during experiments.
- Protein Solubilization:
- Imidazole is known for its role in solubilizing proteins, particularly in the elution step during protein purification processes.
- Structure:
- Imidazole's chemical structure contributes to its ability to coordinate with metal ions, making it useful in certain biochemical applications.
When working with chemicals, it's crucial to follow safety guidelines, use appropriate protective equipment, and handle them in a well-ventilated laboratory setting. Additionally, always refer to the specific product's Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for detailed information on handling, storage, and safety precautions.